Cloudy Pad architecture overview
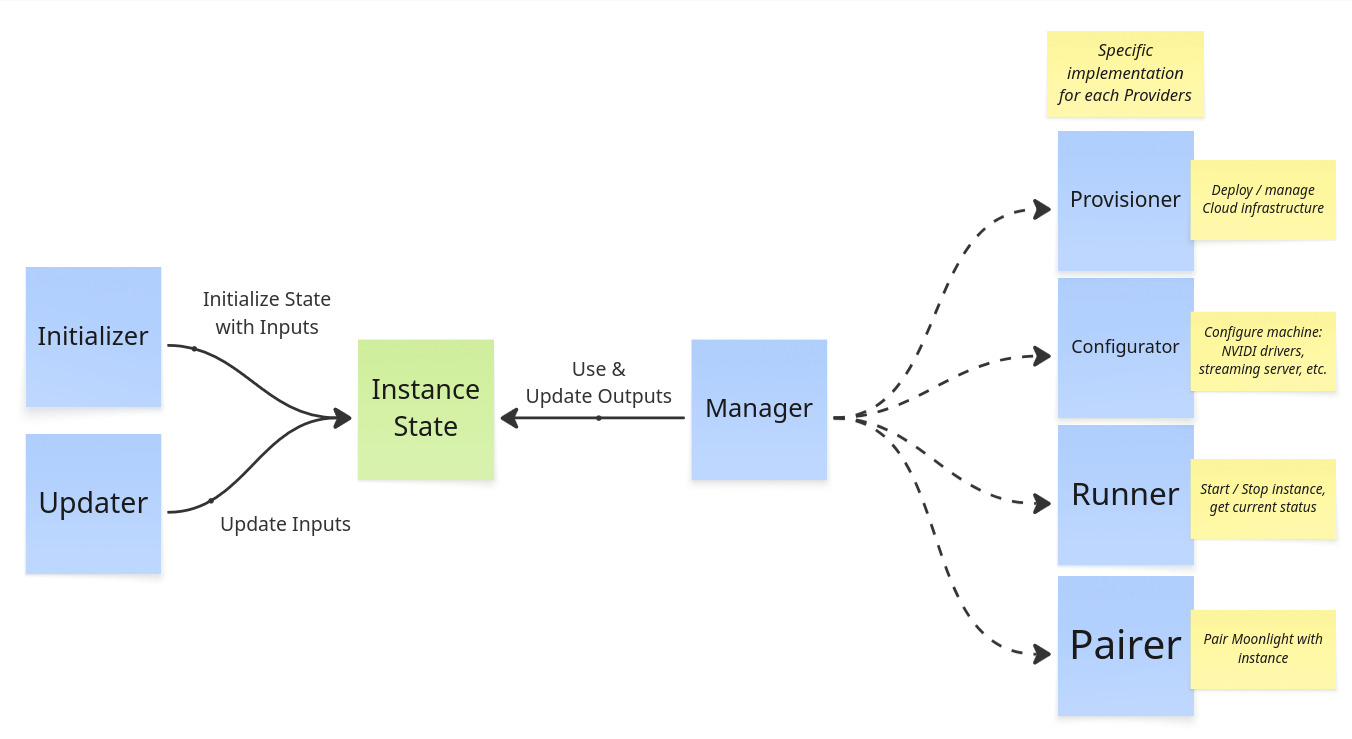
Cloudy Pad code has 3 main parts:
- Core - Internal components to manage instances and deployment
- Provider implementations - implementation of instance deployment and management for various Providers
- A Provider is a specialization of Core components to deploy instances in a given context
- For example
awsProvider is the implementation of instance deployment on AWS (Amazon Web Services)
- CLI - Wrapper around Core components to provide the Cloudy Pad CLI with interactive prompts
Instance lifecycle and Core components
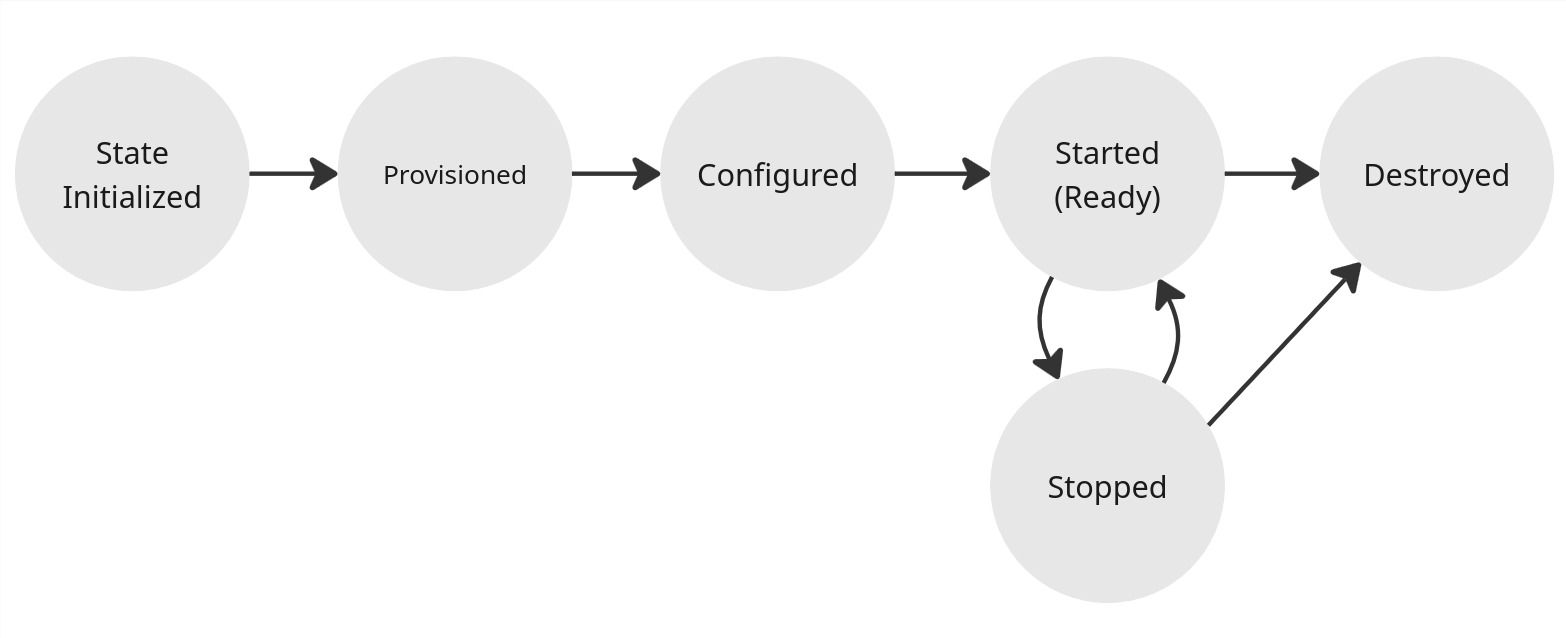
Instance lifecycle:
Initialization (or creation)
An Instance State is initialized with various Inputs (e.g. provider, region, instance type and specs, etc.). On initialization, the instance is:
- Provision - Cloud infrastructure is provisioned (creation of virtual machine, disk storage, etc. for instance) - most of the time with Pulumi (an Infrastructure as Code tool). Note a Cloud infrastructure is not always required, such as with SSH provider, in which case provisioning is no-op.
- Configuration - Installation of OS-level components: NVIDAI drivers, Sunshine / Wolf streaming server, etc. via Ansible (an Infrastructure as Code tool)
- Pairing - Instance is paired with Moonlight client
These steps can also be run separately (e.g. cloudypad provision)
Related code:
core/initializer.ts-InstanceInitializer- Manage overall initialization and deployment withInstanceManagercore/manager.ts-InstanceManager- manages instance lifecycle with:core/provisioner.ts-InstanceProvisionercore/configurator.ts-InstanceConfiguratorcore/moonlight/pairer.ts-MoonlightPairer
Usage lifecycle: start and stop
After initilialization, instance can be started and stopped.
Related code:
core/manager.ts-InstanceManager- manages instance lifecycle withRunner.core/runner.ts-InstanceRunner- Manages instance start/stop actions
Deletion
Destroy instance. Instance deletion deletes infrastructure (instance, disk, etc.) and related Instance State
Related code:
core/manager.ts-InstanceManager- manages instance lifecycle withRunner.core/provisioner.ts-InstanceProvisioner
Instance State
The Instance State represents the state in which an instance is. It roughly contains:
- Instance name
- Provider name (AWS, Azure, etc.)
- Inputs: desired instance configurations (instance type, region, streaming server, etc.)
- Outputs: actual infrastructure state (disk storage unique ID, IP address, etc.)
Each Provider implements its own state interface based on a common State implementation. State is by default persisted as a local YAML file under ~/.cloudypad/instance/<name>/state.yml
Example State file:
name: aws-instance
version: '1'
# Provision inputs and outputs
provision:
provider: aws # provider name
# Desired instance state for AWS
input:
diskSize: 200
instanceType: g4dn.2xlarge
publicIpType: static
region: eu-central-1
ssh:
user: ubuntu
privateKeyContentBase64: xxx
# Actual infrastructure state
# for AWS, host is instance static IP address and instanceId the EC2 instance ID
output:
host: 18.199.182.227
instanceId: i-0ae901f1799b17fdf
# Configuration inputs and outputs
# used to configure instance
configuration:
configurator: ansible
input:
sunshine:
enable: true
passwordBase64: xxx
username: sunshine
As state is written and read externally, Zod is used to enforce TypeScript typing.
See src/core/state
Provider implementation
A Provider is a specialization of Core components to deploy instances in a given context (usually a Cloud provider). For example aws Provider is the implementation of instance deployment on AWS (Amazon Web Services).
Each provider is based on the same pattern. Example for AWS provider in src/providers/aws:
pulumi.ts- Pulumi is an Infrastructure as Code and provisioning tool (like Terraform) to manage Cloud resources. This file defines the Stack program used for each provider.state.ts- ExtendsInstanceStateV1with Inputs and Outputs specific to this providerprovisioner.ts- ImplementsInstanceProvisionerfor this provider. Use State Inputs to configure and run Pulumi stacks (or create infra with Provider API directly)runner.ts- ImplementsInstanceRunnerfor this provider. Use a Provider specific client to call Provider API to start/stop/... instance infrastructure.cli.ts- CLI implementation for this provider. Define Provider specific CLI args and command implementation (e.g.createarguments which are specific per providers)sdk-client.ts- or in aclient/folder. Provider specific SDK clients to interact with various resources (get server status, list available regions, etc.)
More internal-oriented files:
provider.ts- ImplementsProviderClientfor this Provider.factory.ts- ImplementsProvisionerFactoryfor this Provider.